Beautiful Plants For Your Interior

Understanding Insomnia and Awakening: A Comprehensive Overview
What is Insomnia?

Insomnia is a common sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking up too early and not being able to go back to sleep. It can lead to daytime fatigue, mood disturbances, and impaired functioning. According to the American Sleep Association, approximately 30% of adults report experiencing insomnia symptoms, with 10% suffering from chronic insomnia.
Types of Insomnia

| Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Acute Insomnia | Short-term insomnia often triggered by stress or life events. |
| Chronic Insomnia | Long-term insomnia lasting for at least three nights a week for three months. |
| Onset Insomnia | Difficulty falling asleep at the beginning of the night. |
| Maintenance Insomnia | Difficulty staying asleep throughout the night. |
Causes of Insomnia

Insomnia can be caused by a variety of factors, including psychological, medical, and environmental influences. Stress, anxiety, depression, chronic pain, and certain medications can all contribute to sleep disturbances. Additionally, lifestyle choices such as excessive caffeine intake, irregular sleep schedules, and lack of physical activity can exacerbate insomnia.
Psychological Factors
| Factor | Impact on Sleep |
|---|---|
| Anxiety | Increased worry can lead to racing thoughts, making it hard to fall asleep. |
| Depression | Can cause changes in sleep patterns, leading to insomnia or hypersomnia. |
| Stress | Life events or ongoing stress can disrupt sleep cycles. |
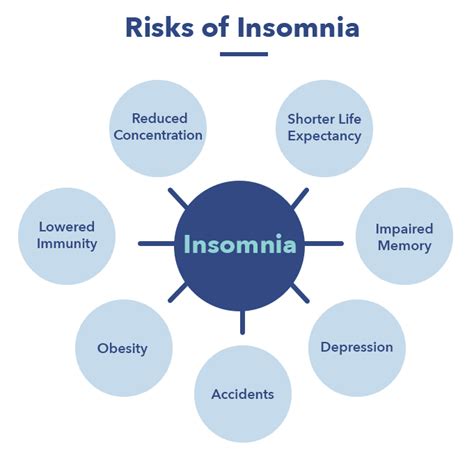
Effects of Insomnia
The effects of insomnia extend beyond just feeling tired. Chronic insomnia can lead to serious health issues, including cardiovascular disease, obesity, diabetes, and impaired immune function. Furthermore, it can affect mental health, leading to increased anxiety, depression, and decreased cognitive function.
Health Consequences
| Health Issue | Connection to Insomnia |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular Disease | Increased risk due to elevated stress hormones and inflammation. |
| Obesity | Disrupted sleep can affect hormones that regulate appetite. |
| Diabetes | Insomnia can lead to insulin resistance and glucose intolerance. |
Strategies for Managing Insomnia

Managing insomnia often requires a multifaceted approach. Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is considered one of the most effective treatments. Additionally, lifestyle changes such as establishing a regular sleep schedule, creating a restful environment, and practicing relaxation techniques can significantly improve sleep quality.
Effective Techniques

| Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT-I) | A structured program that helps identify and replace thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems. |
| Sleep Hygiene | Practices that promote consistent, uninterrupted sleep, such as a regular sleep schedule and a comfortable sleep environment. |
| Relaxation Techniques | Methods such as meditation, deep breathing, and progressive muscle relaxation to reduce stress and promote sleep. |
Q&A on Insomnia
Q: What is Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I)?
A: Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Insomnia (CBT-I) is a structured program that helps individuals identify and replace thoughts and behaviors that cause or worsen sleep problems. It typically involves cognitive restructuring, sleep restriction, stimulus control, and education about sleep hygiene.
Q: What is chronic insomnia?
A: Chronic insomnia is a persistent sleep disorder characterized by difficulty falling asleep, staying asleep, or waking too early, occurring at least three times a week for three months or longer.
Q: What is sleep hygiene?
A: Sleep hygiene refers to a set of practices and habits that promote consistent, quality sleep. This includes maintaining a regular sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and avoiding stimulants before bedtime.
Q: How does chronic pain affect sleep?
A: Chronic pain can significantly disrupt sleep patterns by making it difficult to find a comfortable sleeping position and can lead to frequent awakenings during the night, consequently resulting in insomnia.
Q: What are the common symptoms of insomnia?
A: Common symptoms of insomnia include difficulty falling asleep, frequent awakenings during the night, waking up too early, daytime fatigue, difficulty concentrating, irritability, and mood disturbances.
Q: How does insomnia affect quality of life?
A: Insomnia can negatively impact overall quality of life by causing fatigue, reducing productivity, impairing emotional well-being, affecting relationships, and increasing the risk of accidents.
Q: What are the causes of insomnia?
A: Causes of insomnia can include stress, anxiety, depression, chronic pain conditions, hormonal changes, medications, substance abuse, poor sleep habits, and certain medical conditions.
Q: What is insomnia?
A: Insomnia is a sleep disorder that involves difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep, resulting in daytime impairment or distress.
Q: What are the types of insomnia?
A: Types of insomnia include acute insomnia (short-term), chronic insomnia (long-term), and situational insomnia, which occurs in response to specific stressors or events.
Q: What is long-term insomnia?
A: Long-term insomnia is a persistent sleep disorder lasting longer than three months, often associated with underlying health issues, psychological stress, or lifestyle factors.
Q: How is the term ‘long term’ defined in relation to insomnia?
A: In relation to insomnia, “long term” generally refers to sleep difficulties that persist for several months or longer, requiring intervention or treatment.
Q: What are the side effects of insomnia?
A: Side effects of insomnia can include daytime sleepiness, irritability, difficulty concentrating, increased risk of accidents, and long-term health issues such as cardiovascular disease.
Q: How do sleeping habits affect sleep quality?
A: Poor sleeping habits, such as irregular sleep schedules, excessive screen time before bed, and consuming caffeine or nicotine in the evening, can negatively affect sleep quality and contribute to insomnia.
Q: What health conditions are linked to insomnia?
A: Insomnia is often linked to various health conditions, including depression, anxiety, chronic pain, diabetes, heart disease, and sleep apnea.
Q: What constitutes quality sleep?
A: Quality sleep is characterized by sufficient duration, the ability to fall asleep without difficulty, minimal awakenings during the night, and feeling rested and refreshed upon waking.
Q: What medical conditions can contribute to insomnia?
A: Medical conditions that can contribute to insomnia include asthma, arthritis, gastrointestinal disorders, hormonal imbalances, and neurological conditions.
Q: How does sleep schedule impact insomnia?
A: An inconsistent or irregular sleep schedule can confuse the body’s internal clock, making it harder to fall asleep and stay asleep, which contributes to insomnia.
Q: How does aging affect sleep in older adults?
A: Older adults may experience changes in sleep patterns, such as lighter sleep, more frequent awakenings, and difficulty falling asleep, making them more susceptible to insomnia.
Q: What are some relaxation techniques to improve sleep?
A: Relaxation techniques that may help improve sleep include deep breathing, progressive muscle relaxation, meditation, yoga, and listening to calming music.
Q: Does watching TV before bed affect sleep?
A: Yes, watching TV before bed can affect sleep by exposing individuals to blue light, which can interfere with the production of melatonin, making it harder to fall asleep.
Q: What should I do if I’m having trouble sleeping?
A: If you’re having trouble sleeping, consider implementing good sleep hygiene practices, such as establishing a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable sleep environment, and limiting stimulants.
Q: What amounts of sleep are recommended for adults?
A: Most adults are recommended to aim for 7 to 9 hours of sleep each night for optimal health and functioning.
Q: What insomnia symptoms should I be aware of?
A: Insomnia symptoms to watch for include difficulty falling asleep, waking up frequently, waking too early, day time fatigue, irritability, and difficulty concentrating.
Q: What does lack of sleep lead to?
A: Lack of sleep can lead to several negative consequences, including impaired cognitive function, increased risk of chronic health conditions, mood disturbances, and reduced overall quality of life.
Q: How do mental health conditions relate to insomnia?
A: Mental health conditions, such as anxiety and depression, can significantly contribute to insomnia by affecting sleep patterns and overall well-being.
Q: What constitutes healthy sleep?
A: Healthy sleep involves getting an adequate amount of quality sleep regularly, maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, and using relaxation techniques when needed.
Q: What is acute insomnia?
A: Acute insomnia is short-term sleep disturbance that typically lasts for a few days to a few weeks, often triggered by stress, changes in environment, or illness.
Q: What is daytime sleepiness?
A: Daytime sleepiness is excessive fatigue or drowsiness experienced during the day, often resulting from poor sleep quality or insufficient sleep at night.
Q: What are examples of good sleep hygiene practices?
A: Good sleep hygiene practices include maintaining a consistent sleep schedule, creating a comfortable and dark sleeping environment, minimizing screen time before bed, and avoiding large meals, caffeine, and alcohol close to bedtime.
Q: How does short-term insomnia differ from chronic insomnia?
A: Short-term insomnia refers to sleep difficulties lasting a few days to a few weeks, often linked to specific stressors, while chronic insomnia persists for three months or longer and may require more comprehensive treatment.
Conclusion
Insomnia is a complex condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. Understanding its causes, effects, and management strategies is crucial for those affected. By adopting effective techniques and seeking professional help when necessary, individuals can improve their sleep quality and overall well-being. As the saying goes, “Sleep is the best meditation,” and prioritizing sleep can lead to a healthier, more fulfilling life.

